Behavioral segmentation is a form of marketing segmentation that divides people into different groups who have a specific behavioral pattern in common. Users may share the same lifecycle stage, previously purchased particular products, or have similar reactions to your messages.
Companies combine various marketing channels like email, SMS, messengers, push notifications to give their customers a more significant personalized experience at all touchpoints.
Benefits of Behavioral Segmentation
- Improves targeting accuracy
- Helps provide better-personalized experience
- Sifts engaged users from uninterested
- Saves money
- Makes it easier to track success
- Helps build loyalty to your brand
- Improves targeting accuracy. Behavioral segmentation allows companies to take advantage of behavioral differences, optimizing their marketing messages based on that data. For instance, it helps to pick up the right approach for loyal customers or newly subscribed users. It also clarifies groups of people that make up your audience: adults from 20-34, people keen on sports, or those who love traveling.
- Helps provide better-personalized experience. Mass emails with the same message for everyone are outdated practice today. Instead, you need to deeply analyze your audience and meet people’s demands in a personalized approach based on social groups they belong to.
- Sifts engaged users from uninterested. Marketers filter the target audience to work with by identifying the user’s level of engagement. It increases the chances that your products will be found by people who need them.
- Saves money. Behavioral segmentation helps prioritize campaigns to make your marketing more cost-effective. It allows you to spend less time and fewer resources to warm up leads or trying to communicate with an uninterested audience.
- Makes it easier to track success. You can track metrics inside each segment and improve your results.
- Helps build loyalty to your brand. Behavioral segmentation helps you realize how to support users along their customer journey and keep them engaged all the time. People that are treated personally are more likely to become loyal to your brand and be converted into brand advocates.
Types of Behavioral Segmentation with Examples
- Based on a Purchasing Behavior
- Based on Benefits
- Based on a Lifecycle Stage
- Based on a Level of Engagement
- Occasion-based
- Based on Customer Satisfaction
- Based on Customer Loyalty
You can combine various types of segmentation based on how relevant they are to your business and on specific characteristics of the products and services you promote. Let’s take email as an example for each type of behavioral segmentation since it works for any business from small to large.
Based on a Purchasing Behavior
This segment takes advantage of a users' behavior when they make a purchase.
Check if they hesitate, if there are any obstacles on their way to make a decision. The answer to these and simple questions will help you simplify the buying process.
Let’s point out some common situations when clients are about to convert into customers:
- Considering the best price. This is the most important factor in influencing the buyer’s decision. If you identify people who hesitate by waiting for a better price, you will dramatically increase your chances to make a sale to them during special occasions like marketing holidays, when the prices are reduced.
- Looking for social proof. These users are interested in a product, but they wonder if others are satisfied with the product. To dispel doubts, place customer reviews on your website or right in the email campaign.
- Having all the time in the world. These customers are interested, but they don’t hurry to buy your product. In this case, add a time-sensitive element like adding a countdown to an email, or come up with a time-limited discount. This creates a feeling of urgency.
Below is an example of an automated email triggered when a customer abandons their shopping cart. It is designed to drive people back to the shop to finish their purchase.
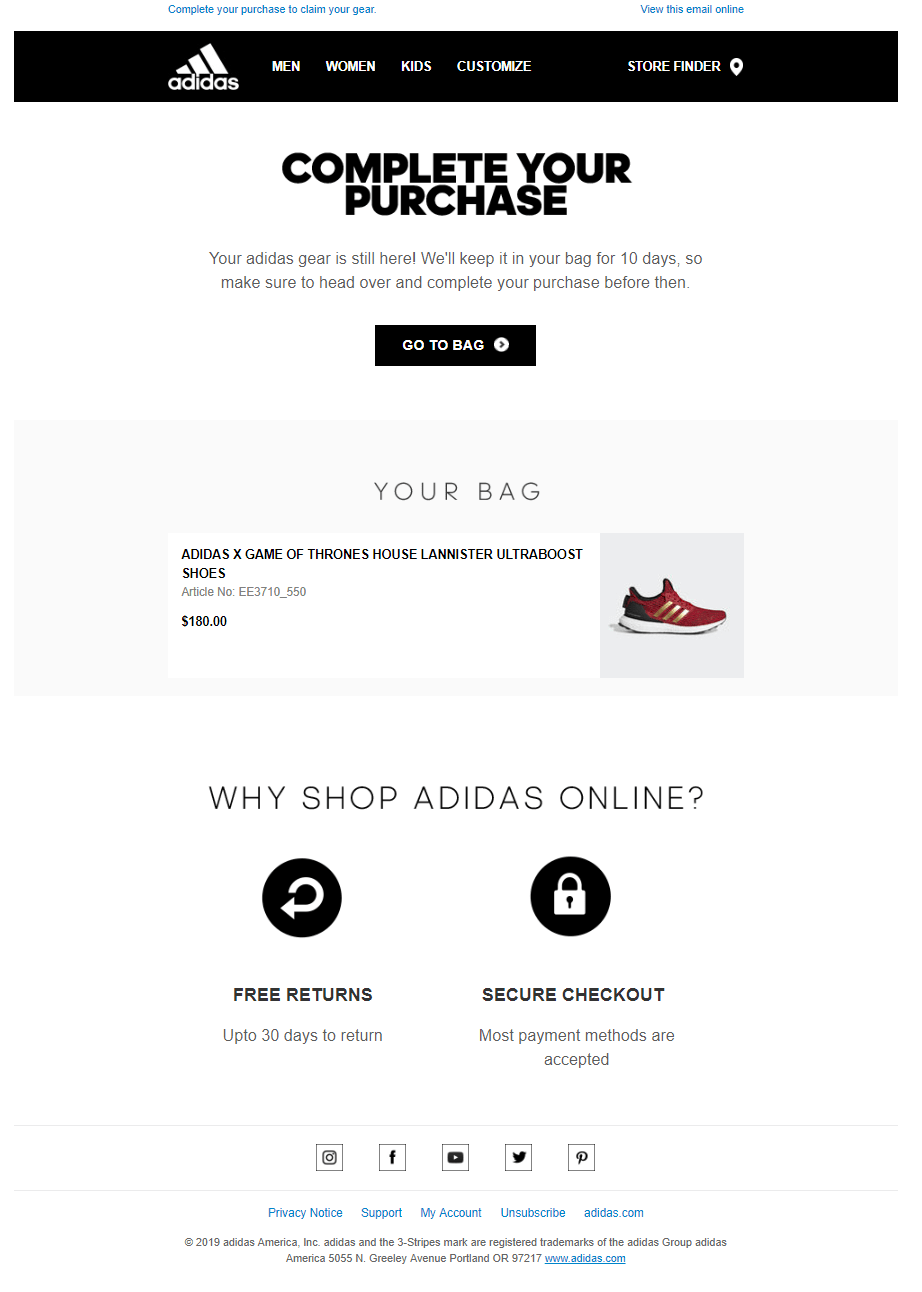
Based on Benefits
This is a way to divide customers according to the benefits they are looking for and motivate them to buy your products or services.
For instance, there are many reasons to buy chewing gum: clean teeth, fresh breath, nice flavor, or anti-stress effect. Find out which benefits drive your customers towards the purchase and emphasize them.
Here’s an attempt to identify what stops a subscriber from using a service — technical issues, lack of features, or not enough motivation.
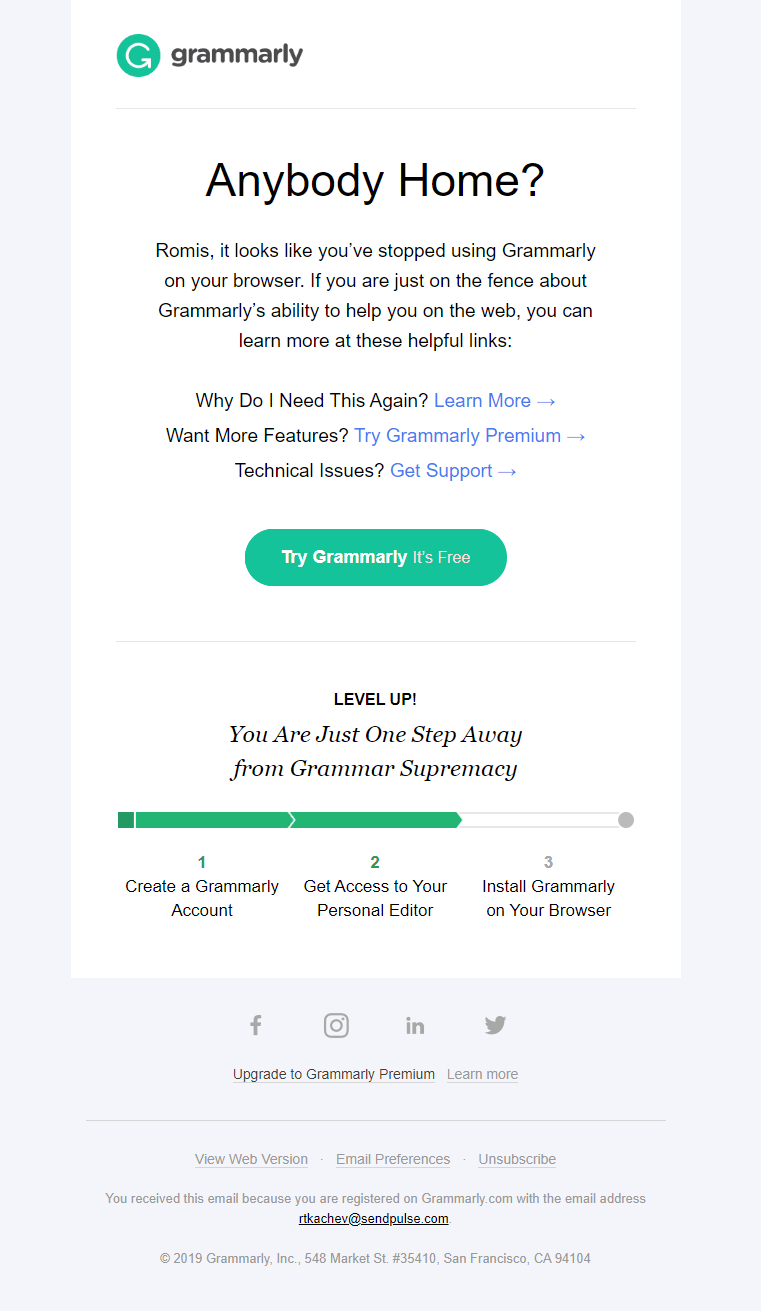
Based on a Lifecycle Stage
Behavioral segmentation based on a lifecycle stage works well for selling products and services with a long lifecycle.
It’s not easy to map user’s lifecycle stage because you can’t judge based on a single touchpoint. To cope with that, collect data on all touchpoints via every marketing channel you use — emails, social media, search engine, chatbot.
When you determine the user’s lifecycle stage, move them closer to the purchase by sending more relevant and valuable nurturing materials and, eventually, offers.
Below is an example of lead nurturing — the lifecycle stage where the company provides educational materials, showing how the product deals with the problems.
Based on a Level of Engagement
This segment is built on how often users log in your service or how many orders they make with your restaurant. Adjust your marketing messages based on this data and encourage user participation. This segment helps reduce the churn rate and improve sender reputation by dividing your target audience from unengaged people.
Let’s check three basic levels of user engagement:
- Occasional. This means that users have a contact with your brand, but it’s not systematic. They may lack motivation or value from your side, so find out the reason with the help of a survey, for instance, and fix it.
- Regular. Users regularly interact with your service, but don’t use its functions to the full extent. Share how-to videos, highlight all features that might be handy for them, and offer a loyalty program.
- Intensive. These users integrate your service in their life, and that is the reason to treat them specially. Provide bonuses, invite to special events, congratulate on their birthdays, because these people may advertize your brand through word-of-mouth and become loyal clients.
The example below is a reactivation email which aims to keep a user engaged.
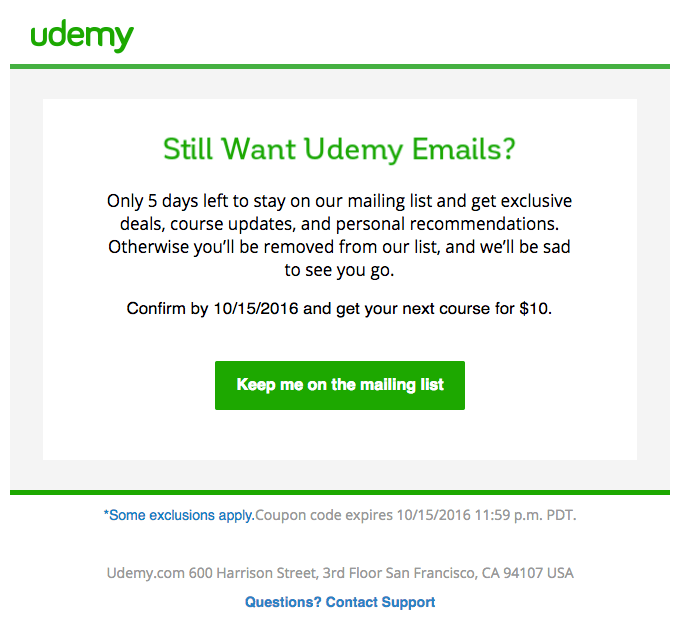
Occasion-based
This is segmentation based on specific timing which is best to deliver your marketing messages.
Utilize marketing holidays like Black Friday, Cyber Monday, or national holidays depending on the user’s location. Take advantage of special dates like their birthday or anniversary. Pay attention to the days of the week and time of the day that is most convenient for communication.
To implement occasion-based segmentation, collect personal data from subscription forms, lead magnets, or surveys. These insights will help you improve the open rate of your campaigns and build a positive brand image.
The example below is a way to use occasion — the end of the year — to upsell a pricing plan.
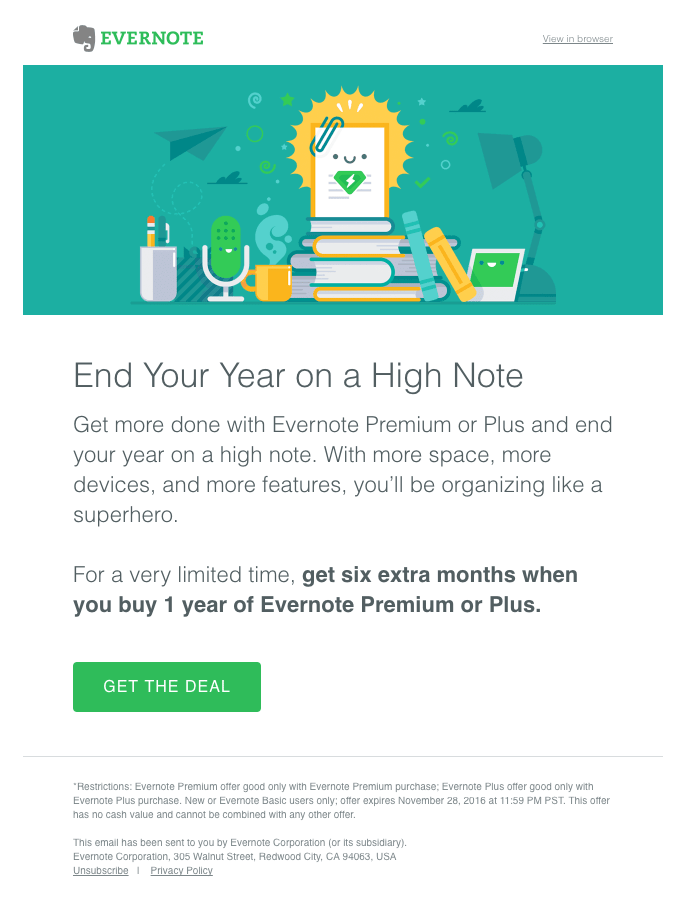
Based On Customer Satisfaction
This segmentation type is based on customer feedback. It helps fix issues when users are not happy with the product before they spread negative words about your brand.
On the other hand, it helps build stronger relationships with other users who already like your brand.
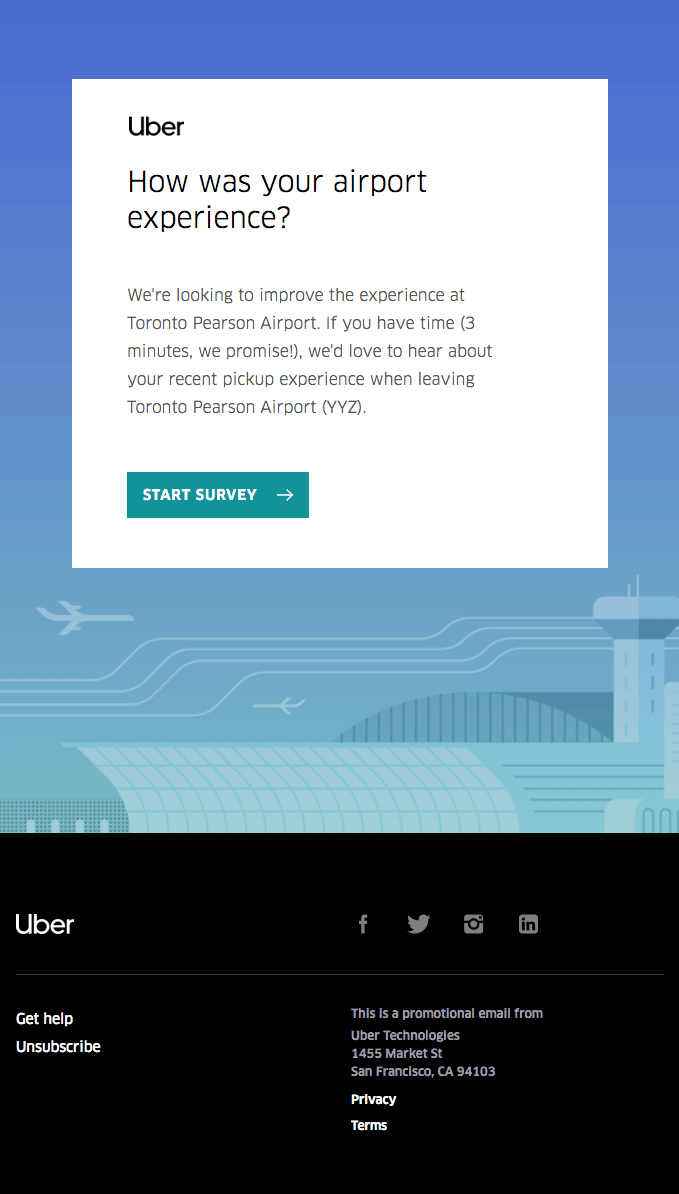
Based on Customer Loyalty
Find out which customers you need to focus your loyalty programs on, and those who may lack value from your brand.
Loyal customers are the most beneficial clients for any business since they have the highest lifetime value. It is cheaper to retain existing customers than acquiring new leads. Also, loyal users are more likely to become brand advocates, and promote your brand around their social circles.
The example below is a way to celebrate cooperation and show a user’s interactions with your brand.
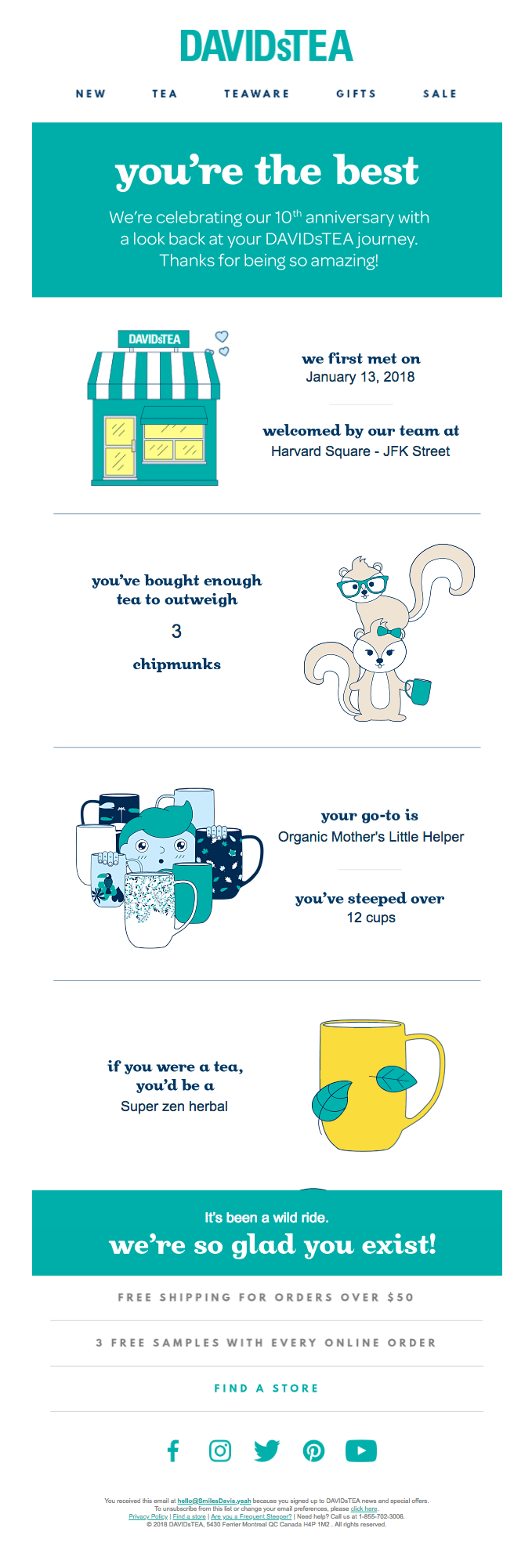
Using Behavioral Segmentation
- Wtih email marketing. Send triggered emails connected with a purchase — abandoned cart emails, confirmation emails, email notifications, and more. Aside from that, try using drip campaigns to welcome users, reactivate them, upsell and cross-sell goods.
- With SMS marketing. Track how people react to your SMS advertising campaigns. Divide your audience into segments based on whether they used your promo codes or not, and try searching for other ways to contact unengaged users.
- With SMM. With Facebook advertising, for instance, you can tailor your ads to people based on how they engage with your posts. If users often respond, encourage them with a discount.
- With chatbot marketing. While users communicate with your chatbot, you can narrow their path towards solving the exact problem. When the conversation ends, you will identify the user's lifecycle stage, making it easier to find the right approach for the next touchpoints.
References
- The article "Defining Behavioral Segmentation with 7 Examples from Marketing Campaigns" by Instapage explains why behavioral segmentation is so important in marketing.
- The article "The What, Why, and How of Behavioral Marketing" by HubSpot defines the term and gives insights on how it works.
- The article "Behavioral Marketing: a Closer Look at What Gets Consumers Clicking" by Neil Patel unveils the very essence of behavioral marketing.

or