Direct costs are expenses that can be easily assigned to the production of a specific product or service. These costs are often variable and fluctuate based on the production level. Examples include expenses on raw materials, manufacturing and packaging supplies, credit card fees, etc.
In this article, we’ll compare direct and indirect costs and review the examples. We’ll also unveil how to calculate and reduce direct costs.
Why are direct costs important?
Knowing direct costs helps you make the right business decisions and develop a relevant marketing strategy. Before producing the products and selling them to your customers, you need to calculate your expenses for the manufacturing process. After you identify the total spending, you can determine the price and the number of items you need to sell to cover the expenses and receive good revenue. So to recoup the costs, you need to be aware of each dollar you spend to produce goods.
You should keep an eye on direct costs to determine whether the production price stays the same or increases. When the expenses for product manufacturing rise, you should review your product pricing. If you don’t monitor fluctuations in the prices of supplies, your profits might decrease. To avoid this scenario, estimate direct costs every month to make sure that they have no changes.
Now that you know why it’s vital to keep track of your direct costs, it’s time to get to know the difference between direct and indirect costs. After reviewing the next section, you’ll see distinctive features and will be able to differentiate them in your business.
Direct Costs vs Indirect Costs
Entrepreneurs often neglect the difference between direct and indirect costs. However, it’s essential to identify and be aware of these expenses. In this section, we’ll make the difference clear.
Direct costs are expenses directly associated with producing a specific product or service. These costs tangibly contribute to the manufacturing process. Examples include commissions, raw materials, labor, transportation, fuel, certain utilities, etc. For example, a brand needs cocoa mass, cocoa butter, and sugar to produce chocolate. To print books, a company needs paper and ink.
Indirect costs are expenses that can’t be directly tied to the manufacturing process of a specific good or service. However, they are critical since support the existence of a business and fulfill operational needs. Examples include business insurance, building rent, office equipment rental, security costs, accounting, maintenance, administrative costs, etc. For instance, if a company has problems with equipment, having business insurance will prevent it from huge repair expenses. Insurance doesn’t have a direct connection to the product, but a company can’t freely operate without it.
Now that you know the difference, let’s review how to estimate direct costs. It’ll help you identify your major expenses and find ways to reduce them and optimize your budget.
How to calculate direct costs?
Direct costs make up the most significant part of your budget for product manufacturing, so it’s critical to track them. The easiest way to estimate these costs is by summing up all money you spend to buy raw materials and pay wages. Identify all expenses that directly contribute to the production of your product. Since calculating direct costs is essential for your marketing strategy, pricing, and revenue, we’ll provide you with a short step-by-step guide.
- List all costs associated with the manufacturing process. Before preparing a budget, you need to consider all possible costs involved in the production process of your goods. Make sure to list all of them to calculate the right price for your products. Pay attention to materials’ cost, labor cost, sales commission, packaging supplies, etc.
- Write down the value of each. Find the accurate prices for all supplies and mention them in your list. To optimize expenses, you need to have exact figures.
- Sum up all expenses on your list. Add up all costs you spend to manufacture your product. The sum of these contributes to the manufacturing of your goods. With this indicator, you can make the right business decisions regarding pricing, materials, vendors, salaries, and profits.
Let's imagine you have a company with the following cost object.
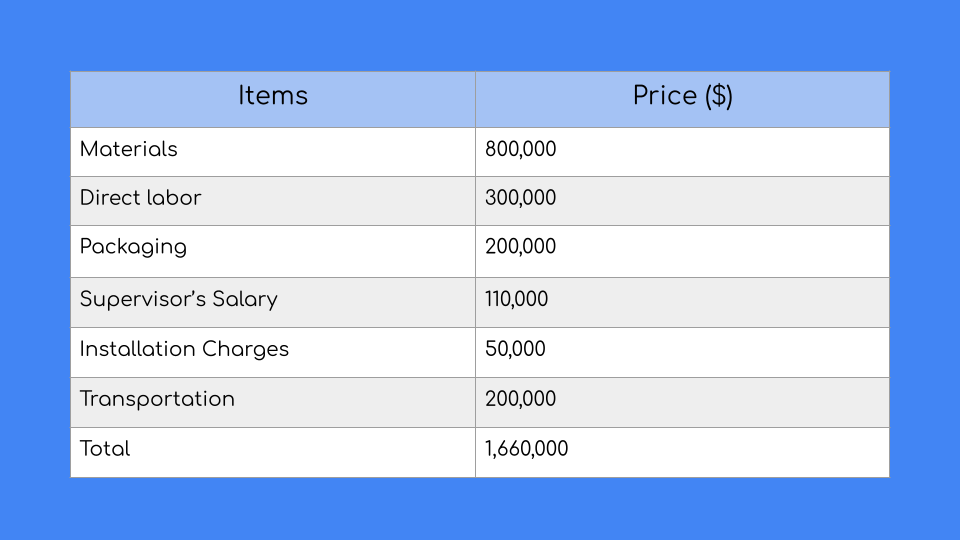
So, the total of your direct costs will be $1,660,000. You need this sum of money plus indirect costs to produce your products.
Now that you know how to estimate production costs, it’s time to unveil some examples. With their help, you’ll make sure that the expenses you identify as direct are right.
Examples of Direct Costs
Direct costs are the basis of proper company operations. They play an important part in budget calculations, price determination, revenue estimations, and more. This section will review some prominent examples of direct costs that can be easily identified within a specific product or service.
The production of a specific product is possible when the company has all the necessary raw materials. The quality of materials might vary, but a company should have them. For instance, to make tables, a business needs to buy all the materials, including wood, glass, stainless steel, etc.
Transportation costs are also examples of direct expenses. These costs are associated with specific ready-to-use items moved to their owners. Every dollar spent is included in the cost of the product. The shipping of materials and changes in production and sales locations are calculated as transportation costs.
Now that you know the examples, it’s time to jump into the next section. After reading it, you’ll figure out how to reduce direct costs and increase revenue.
How to reduce direct costs?
Constant changes within the market, fluctuations in prices, and customer demand urge companies to keep an eye on direct costs. This enables them to adapt their pricing and receive profit from sales. Once identified, entrepreneurs search for ways to reduce direct costs and encourage business growth. We’ll provide you with the steps that will help you with this.
- Negotiate with suppliers. You can reduce direct costs by reviewing your contracts. Revise the list of your vendors and the prices they offer. If you think that some suppliers' prices are too high and influence the profitability of your business, conduct negotiations. Ask vendors to provide you with discounts for making big orders or long-term cooperation. You can also talk with them about free shipping. If the answer is negative, then consider other suppliers and their offers. Once you find vendors that meet your expectations in terms of price and quality, consider cooperation with them.
- Manage inventory properly. To avoid big inventory expenses, ensure you don’t have overstocking. Customers won’t buy an old stock at full price and you can have problems with revenue. To save yourself from unnecessary costs, always consider customer demand. Research what products and in what quantities are sold fast and which are rarely bought. Make demand forecasts to identify the number of products your company needs. Consider using software to track stock in real-time and take action when you have overstock. It’s critical to sell old items with discounts, special offers, and seasonal sales to get your money back.
- Ensure proper logistics. All parties involved in the production process should have access to the transportation information. This way, they’ll make sure that goods are manufactured, packed, and shipped to end users without delay. Your company needs a centralized logistics hub, insurance, and trusted carrier.
Now you know what direct costs are and why they are critical for business. Hopefully, you’ll implement our tips right to prevent a decrease in business profitability, wrong budget calculations, and wrong business decisions.
References:
- This article defines the term and uncovers how direct cost works.
- In this article, you’ll find types of direct costs and the formula to calculate them.

or