Every site owner wants an SEO-optimized website. Any gains in search rankings can result in thousands, if not millions of dollars in profit. Unfortunately, the reverse is also true. If anything goes wrong, the whole company suffers. You’ll lose thousands of dollars, if not millions.
If you’re a webmaster facing a massive drop in your Google rankings, then your website may be facing some SEO issues. The good news is that, often, you are facing a common problem that is easy to resolve with the right approach. This article will review seven common SEO issues webmasters face and their solutions.
Keyword cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization occurs when multiple web pages from the same owner are competing for the same query on search engine result pages (SERPs).
Let’s say you have two guides to SEO. One of those guides was published three years ago, and the more recent guide was published last month. That may cause a problem.
You now have two pieces of content addressing your audience’s pain points but targeting the same keyword. That’s a problem because when Google crawls and indexes your site, it will try to credit both pages. The problem is, it won’t be able to decide which is more important.
Now, you may ask why can’t both pages rank on the first page together?
Technically it’s possible. However, your two pieces of content need to fill different needs. For example, you could have a sales page and a blog post targeting the same search term. One page fulfills a user’s desire to purchase, transactional, while the other fulfills an educational purpose.
Here’s a great article about the SEO strategy Canva implemented that discusses this topic and shares many examples. Below is a screenshot of two different pages targeting “designing certificates.”
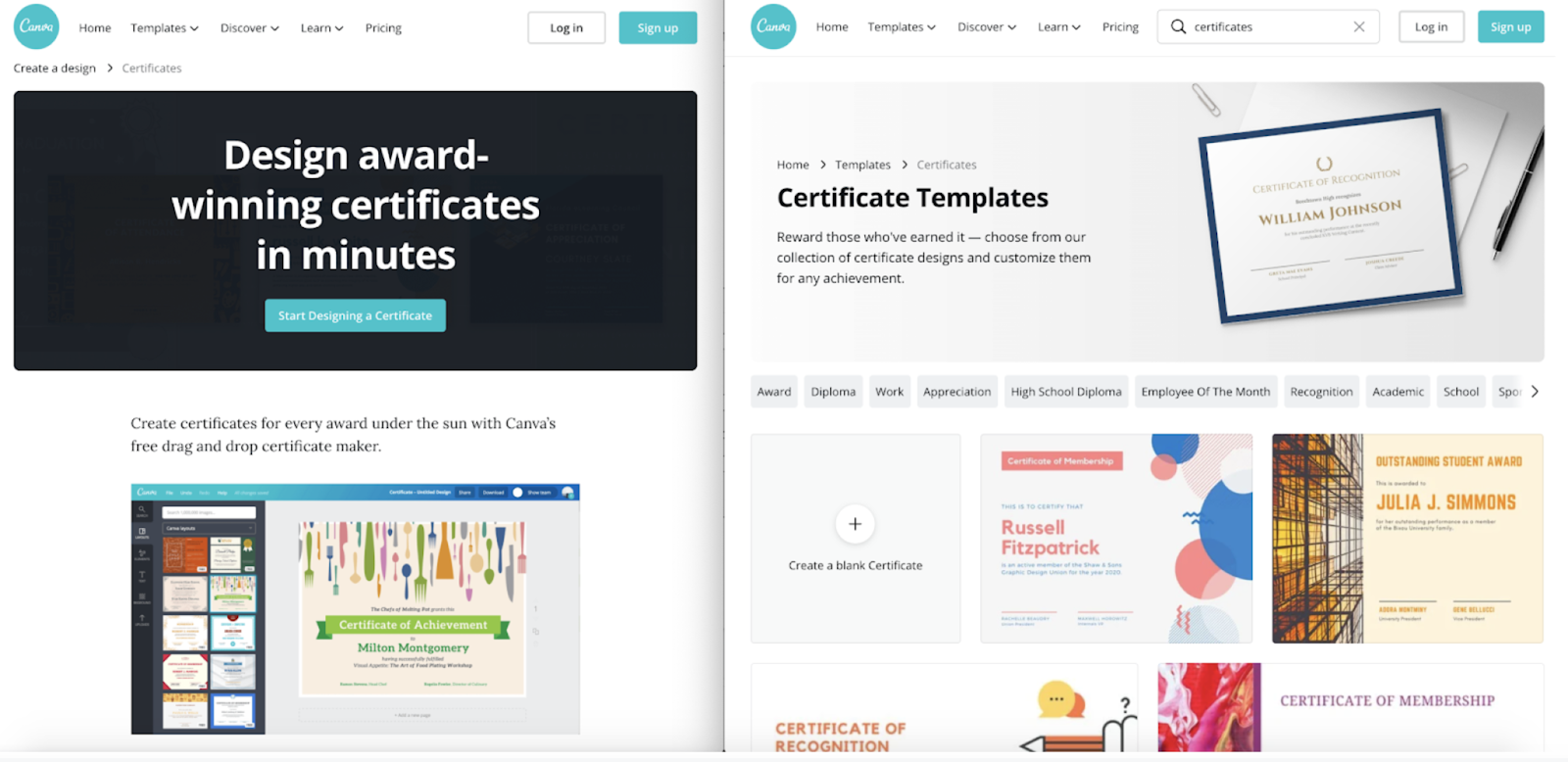 Two different pages both targeting “designing certificates;” source: Foundation Inc
Two different pages both targeting “designing certificates;” source: Foundation Inc
Each page fulfills a different user desire.
David Campbell, Marketing Strategist at Right Inbox, recommends only creating multiple pages targeting the same keyword when you are fulfilling different search intent. If a person is only searching for a term for educational purposes, it does not make sense to have two pieces of content fulfilling the same role.
When this occurs, you have a problem with keyword cannibalization.
If you want to see which pages of your website face this issue, go to your Google Search Console. Type a query and go to the Pages section. If you find more than one web page listed there, then you’re facing keyword cannibalization.
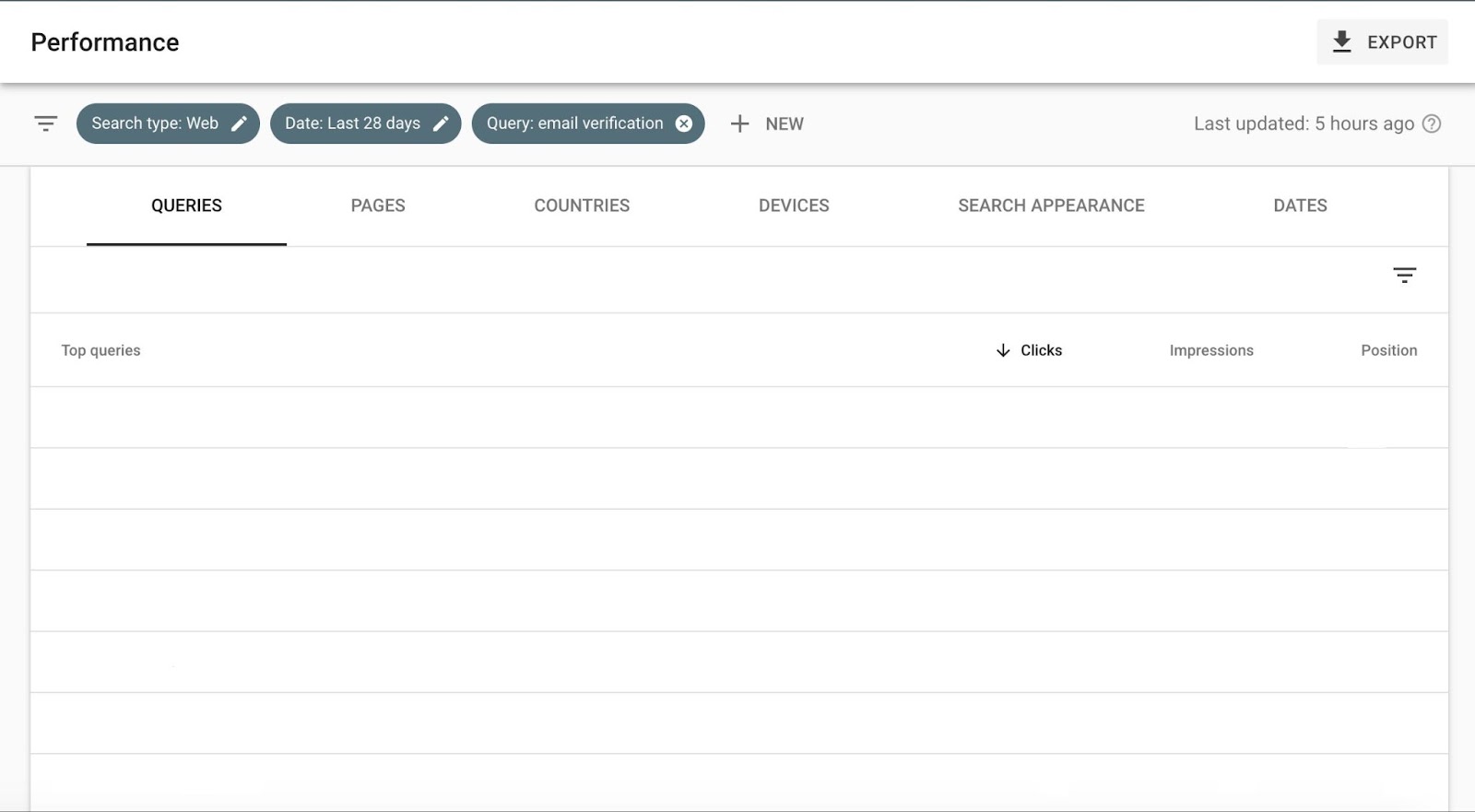 Google Search Console can show website pages facing keyword cannibalization issues
Google Search Console can show website pages facing keyword cannibalization issues
To solve this problem, optimize your pages so that they don’t compete against each other. For that, you can do at least one of the following:
- Go over your titles and descriptions and make them unique.
- Combine two blog posts into one if they are about similar topics, or make them focus on different keywords.
- Check the anchor text of your internal links. Make sure the anchor texts follow the best internal linking practices. Two different anchor texts should point to two different web pages on your website.
- Check your backlinks. The same rules for internal links apply to external links too.
Keyword cannibalization mainly happens to websites with lots of pages. The issue is quite easy to resolve by spending a little bit of time on your website.
Over-optimized anchor text
Overly-optimized anchor text is a sign of big trouble. Overly optimized anchor text means that the anchor text for your links on other websites is the same or very similar.
Let’s say you have a page on B2C marketing. You’ll want to rank for the query “B2C marketing” on Google and other search engines. Let’s say that you decide to build links for the web page using the anchor text “B2C marketing.”
The result? A problem.
Google is strict. Over-optimized anchor text shows you are trying to manipulate Google’s search algorithms. That may result in your content being penalized or even completely removed from Google’s index.
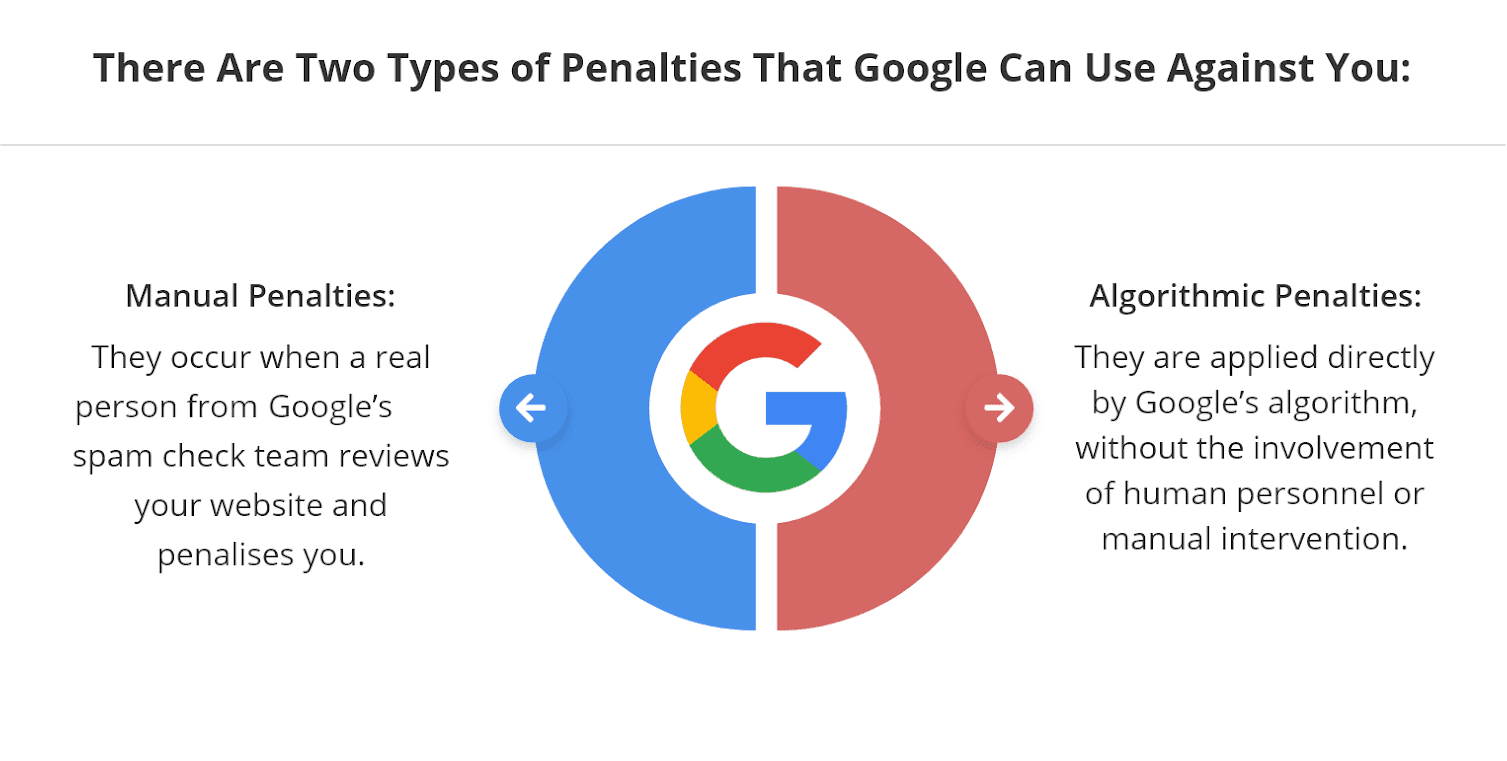 A graph from Devrix showing the ways Google can penalize you; source: Devrix
A graph from Devrix showing the ways Google can penalize you; source: Devrix
How do you detect the problem?
You can use an SEO tool like Ahrefs. Put your website address in Ahrefs address bar and search. Find the Anchors option in the panel on the left. Click, and you’ll see all the anchor text where your webpage link is placed.
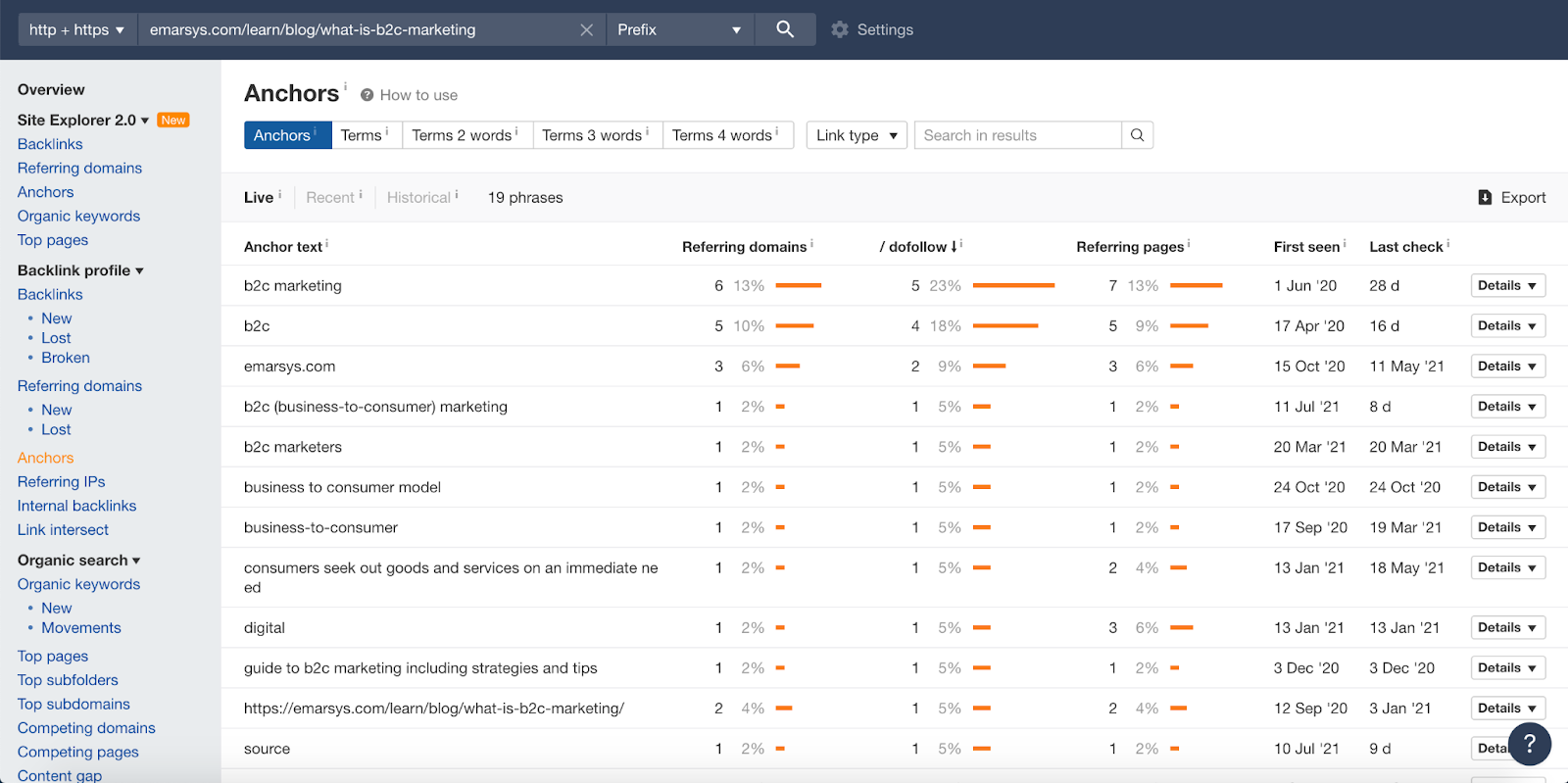 Ahrefs results showing the varied anchor text where a page link is placed
Ahrefs results showing the varied anchor text where a page link is placed
You can see that this page ranking for the term “B2C marketing” has varied anchor text.
If you have overly-optimized anchor text, you need to make some changes. For internal links, use synonyms. Alternatively, you can create long anchor text containing your keyword.
As you’re in full control of internal link building, you can do the optimization quickly. As far as backlinks are concerned, you’ll have to reach out to bloggers and ask them to help you in updating optimized anchor text. You can use an email finder to find their contact details and send a message.
Slow page speed
Your website’s page speed is important. People are impatient and don’t wait around for a slow site to load. It’s a user experience issue, and it impacts search rankings.
Your website should load quickly. Preferably in less than two seconds. One of the best tools for checking your site speed is Google PageSpeed Insights and GT Metrix. Both tools do pretty much the same thing, they:
- show you how fast your site loads;
- identify issues that are slowing your site down.
You can use the insights you gain from running a test to improve your page load speed.
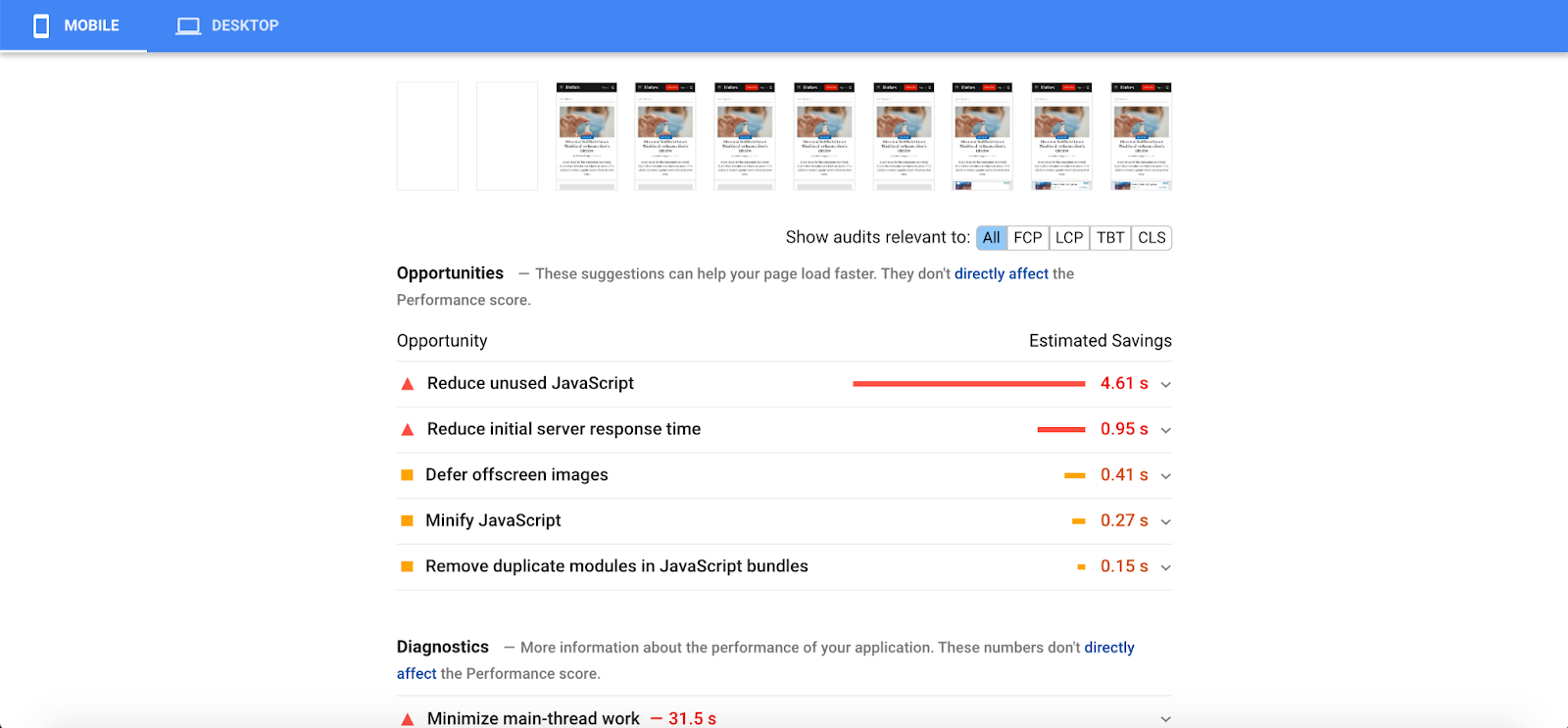 Pagespeed Insights test results of a sample page
Pagespeed Insights test results of a sample page
You may need a developer to implement some of these recommendations.
Thankfully, you don’t have to be an expert to improve your website speed. Tools like Nitropack that work on WordPress, for example, automatically optimize your site. All you need to do is install the plugin, press activate, and your page speed issues will no longer be a problem.
Problems with your images
Images are important. They help make content engaging. However, they can also be a cause of problems for your site.
One of the main issues you should consider is image size. The larger the image file size, the longer it will take for the page to load. There are various ways to address this issue.
Firstly, you could host images offsite. For example, WordPress has a feature that allows you to host your images on the WordPress server. That means your images are loaded a lot faster than they would be if hosted on your site.
The second thing you can try is to defer to offscreen images. Deferring offscreen images means that images only appear on the screen load when a person accesses the page. Images off-screen will load as the person scrolls down the page. That means your page will take less time to load as the initial file size is smaller.
Finally, you can optimize your image size. There are two ways to do this. The easiest option is to use a suitable plugin that optimizes your site images. If you’re using WordPress, you can use a plugin like Smush. There are plenty of alternatives to this plugin.
Alternatively, you can optimize your images offsite. You can use a tool like Pixlr to do this.
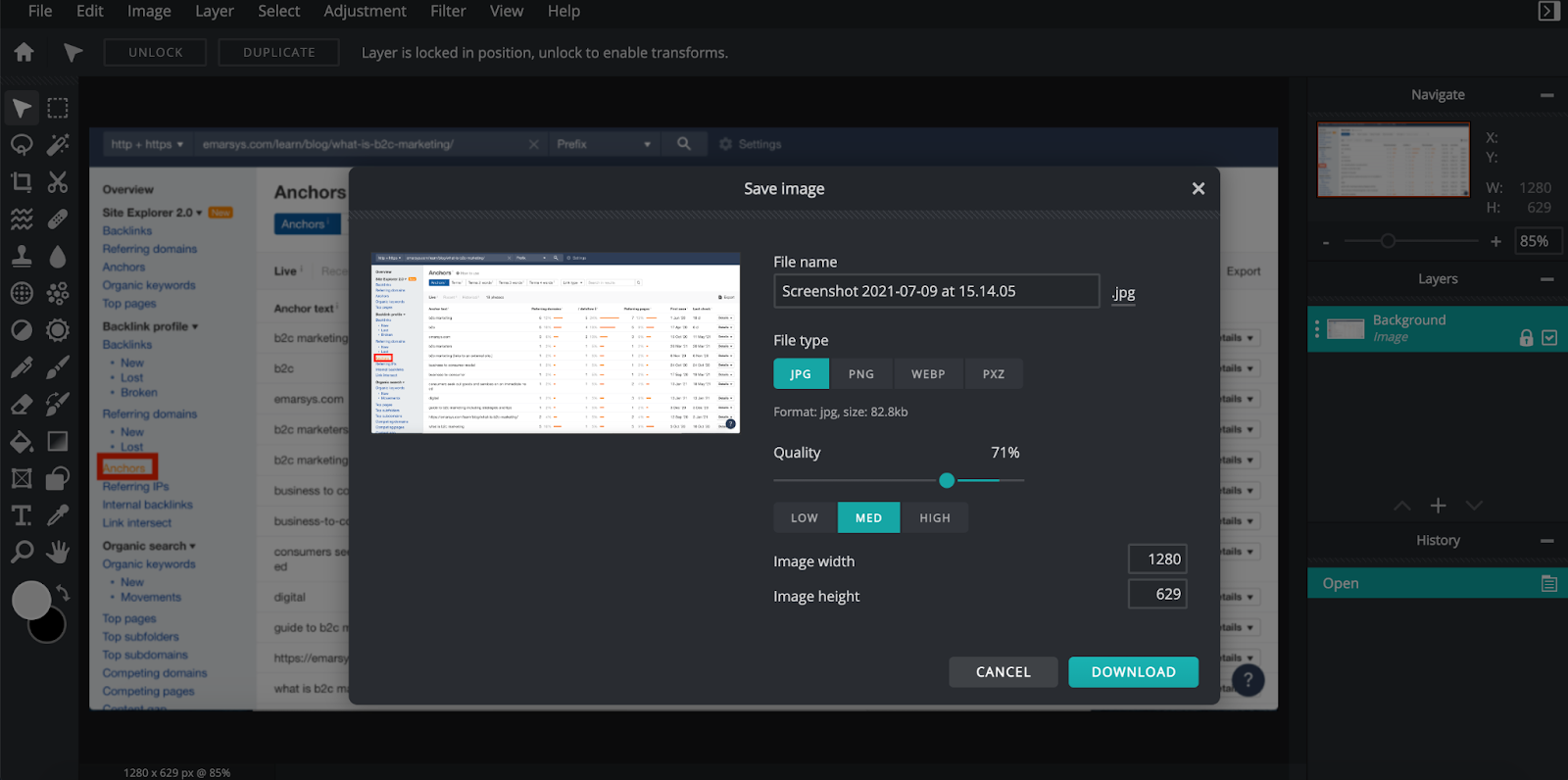 A screenshot showing how you can resize an image
A screenshot showing how you can resize an image
Every website has a different idea of the perfect image size. I’d recommend ensuring your images are smaller than 300kb each. Ideally, they should be half of that or less.
The second thing you need to do is name your images. This is important because a search engine crawler doesn’t see an image — it only sees the source code.
While naming your images is less important for SEO now than it used to be, it’s still something you should do. Plus, people who have issues with their vision will appreciate the gesture.
Broken links
One common issue that you should regularly review and try to resolve on your website is broken links. Broken links are bad because they direct people to content that doesn’t exist.
People don’t like visiting pages with no content. It provides a poor user experience.
Broken links are also a problem for SEO. Moreover, you are wasting your page authority by offering links to nothing.
Page authority flows through both internal and external links. When the authority is directed to a page, it can help boost the search rankings of content.
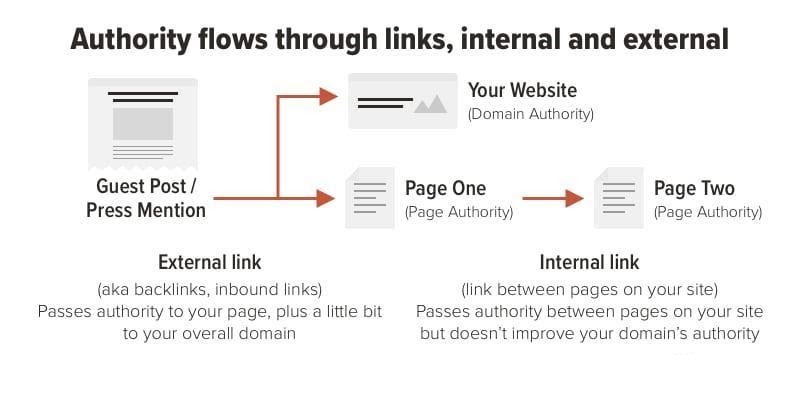 A graphic showing how authority flows through links; source: Orbit Media
A graphic showing how authority flows through links; source: Orbit Media
Thankfully, fixing broken links is straightforward.
To fix broken internal links, you need to crawl your website. Various SEO tools have a crawler that allows you to check for broken links on your website. Some of the most used tools include Morningscore, Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, SEMRush, Serpstat, and Moz.
There are plenty of alternatives to the tools I just mentioned, and lots of free tools as well.
When you do a crawl, you can identify pages that have broken links. All you need to do once you’ve identified a broken link is update the URL to the correct page. Problem fixed.
The process for fixing broken external links is straightforward as well.
One option is to set up a 301 redirect. It will redirect people who would have visited a broken page to the correct page. A 301 is a fast solution to a problem. You should try to reach out to sites that link to the outdated content and ask them to update the link as well. You might have to send multiple follow-up emails to get a positive response.
Duplicate content
Duplicate content is when a piece of content appears in more than one place on your site. Google doesn’t penalize you for having duplicate content on your website. However, having multiple versions of the same content on your site can harm search rankings because Google doesn’t know which version you want to rank for.
The second way duplicate content can harm your search rankings results from link equity. For example, imagine 50% of external links go to one piece of content and 50% of external links go to a second piece.
Clearly, it would be better to have 100% of your links going to the same content.
Various factors can cause duplicate content, and the solutions are just as varied. Rather than taking a deep dive into this topic, I recommend you read a handy guide on duplicate content by Moz and implement the relevant solutions if you have a problem.
Toxic or spammy backlinks
Backlinks can both harm and improve your search rankings. If you get the right type of backlinks from authoritative sites, you will likely see a boost in your search rankings. That’s a positive. It’s why people invest so much energy in blogger outreach and other types of link building.
High Authority links can be a major differentiating factor from sites that are spun up overnight.
SourceKelsey Libert
Co-Founder at Fractl
It works, too.
Unfortunately, not all links are positive.
Links from spammy domains that link to all types of sites can harm your search rankings. If you have these types of links pointing to your site, you need to do a disavow.
Now, doing a disavow is an advanced SEO strategy. Google specifically warns you about the potential negative implications of a disavow through the Google Search Console dashboard.
However, it can benefit your rankings. The easiest way to do a disavow that I’ve discovered is to head over to Fiverr. You can pay someone to create a list of toxic links. You’ll be given a list of sites. Before implementing the disavow, review the sites on the list.
You should include sites that:
- link to all types of third party sites;
- post terrible low-quality content;
- have a low Trust Flow;
- look like they’ve been hit by a Google penalty — they might have seen a sudden and drastic drop in traffic, for example.
Once you have a list of these sites, open Google Search Console and upload your disavow file. A disavow can result in a sudden jump in traffic because you’re no longer being held down by links from less-than-ideal sources.
Conclusion
If you’re running a website, you probably invest resources into content marketing and SEO. Unfortunately, many websites suffer from common SEO issues that negatively impact search rankings. Fixing these issues can generate a sudden boost in traffic.
This guide walked you through seven common SEO issues that may be affecting your website and how to resolve these issues. We discussed factors like page speed, broken links, duplicate content, and keyword cannibalization. Fixing these issues is a quick and easy way to boost your search rankings.