A data breach that impacted half a billion Facebook users in 2021 leaked full names, birthdays, phone numbers, and even their location. Facebook suffered a public backlash, hefty fines, and a soured reputation for data security. Concerning customer data management, don’t be like Facebook.
It’s no secret that securing customer data is a complex and challenging task. With the rapid technology growth and interconnectedness of the internet, your customer’s data security is an even more significant concern than ever before.
This post reviews the importance of customer data management and the five best practices for securing customer data. Let’s dive in.
What is customer data management?
Customer data management, or CDM, is the process of managing customer data across the entire customer lifecycle. It includes collecting, storing, and using information about customers, prospects, and their interactions with your organization’s products and services.
Data is everywhere in today’s business world. It’s on mobile devices, laptops, desktops, and servers — it’s in emails and third-party systems such as CRM software solutions — it flows into marketing automation platforms — it lives in product databases and sales force automation (SFA) applications.
Organizations struggle to keep track of data while maintaining security and privacy protection.
There are four main challenges to ensuring customer data security:
- the amount of customer data that’s collected;
- the number of people who need to access the data;
- a lack of centralized systems to manage it all;
- a lack of culture around privacy and security.
Thankfully, there are simple yet effective ways to protect and secure customer data in an increasingly digital environment:
- use strong passwords and change them often;
- encrypt data when storing or transferring it;
- use two-factor authentication whenever possible;
- train staff members on proper data handling practices.
Remember that these tips should be the foundation of your CDM strategy. Later in this post, we will dive deeper into a few additional best practices to enhance your data management for maximum security. But first, let’s review the type of data you are collecting from your customers to understand how to keep it safe.
Four types of customer data
Customer data plays a crucial part in running any business.
You need to know who your customers are and how they behave to provide them with products and services that meet their wants and needs. You also need to know what they think about your company and its offerings so that you can make improvements when necessary.
Customer data comes in many different forms, but there are four main types that every business should consider when looking at their customer information.
Basic data
Basic data is the foundation of customer data. It includes things like name, address, email, and phone number — core details that make up an individual customer.
Engagement data
Engagement data is the actions customers take with your company. These actions include the type of products customers buy, their purchase frequency, and the purchase’s value. You can use engagement data to improve customer experience and identify potential opportunities.
Behavioral data
Behavioral data is a type of information that captures the actions your customers take while interacting with a digital service. This data can help you improve the UX of your product or even help you measure how well it’s working in general.
Use web analytics tools like Google Analytics to track how users interact with your website or app. For example:
- What pages had the most visitors?
- How long do people stay on each page?
- What happens when they click a CTA?
Behavioral metrics give insight into user behavior but don’t provide any context for why this behavior occurs. If someone spends more time on a particular webpage than others, it could be because they found information there that was valuable to them (or it could just be because they have a slow internet connection).
Attitudinal data
Attitudinal data is information about the consumer’s opinion. Use surveys, focus groups, and interviews to understand how consumers feel about a specific product or service.
Attitudinal and behavioral data are both quantitative and qualitative in nature.
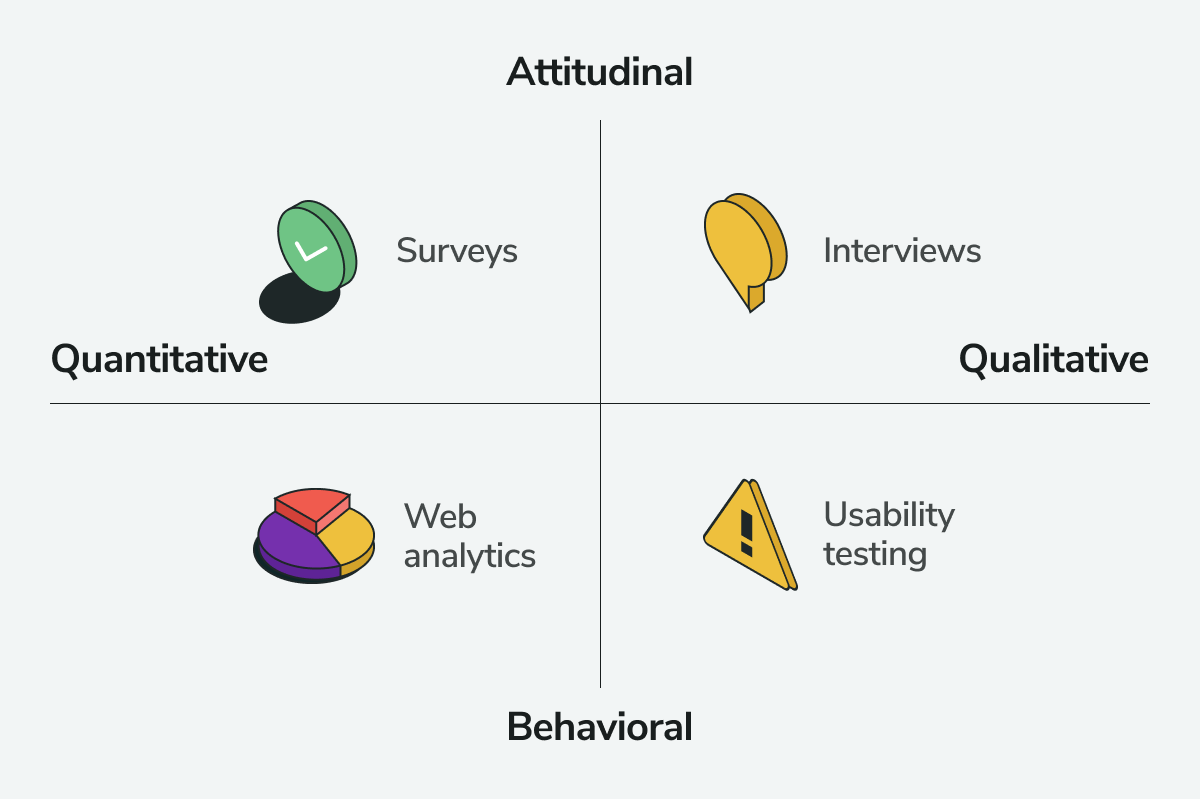 Leverage different tools to capture each category of customer data
Leverage different tools to capture each category of customer data
For example, suppose you’re selling an energy drink. If so, get attitudinal data on your target market’s satisfaction with the product. It’ll help you understand how much they like or dislike the new flavor or the amount of energy it provides. Use this information to help perfect future product offerings.
Five best practices for securing customer data
The more you know about protecting customer information, the better prepared you’ll be to avoid data breaches or other security risks. Below are five best practices that every business should follow to keep their customers’ data safe.
Conduct a data audit
A data audit is a thorough review of your organization’s data to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities. It can be an in-depth process that takes weeks or months, but the benefit is twofold:
- avoid costly mistakes by identifying the areas where you need to improve;
- make sure that all of your company’s information assets are adequately secured.
You should conduct a data audit at least once a year to make sure everything stays on track by following the audit framework.
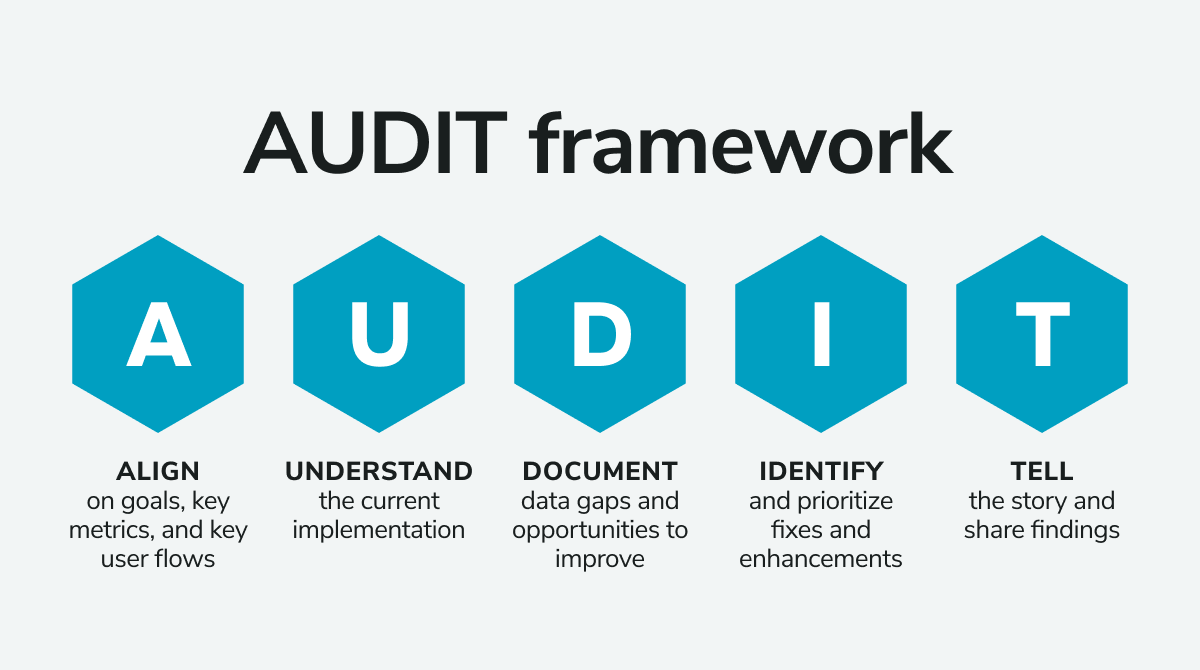 Stay on track by following the AUDIT framework
Stay on track by following the AUDIT framework
Before you start, determine the scope of the audit by figuring out which systems and applications need auditing. Suppose there are any third-party vendors involved in storing information on behalf of your organization (for example, with cloud storage). In that case, these should also be included in this process and any third parties with whom you share personal data, like lenders or health insurers.
Once you know the scope, it’s time to identify areas where risks may exist so you can develop appropriate solutions.
Don’t worry. An annual data audit should easily display these gaps and allow you ample time to implement additional security measures to resolve potential threats.
Implement a data governance framework
Data governance is the process of setting standards and procedures to ensure the security of data. It’s also a risk management process that guarantees your organization stays compliant with regulations like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
The goal is to create a comprehensive framework for managing data, which includes defining roles, responsibilities, policies, procedures, standards, and guidelines for handling sensitive information.
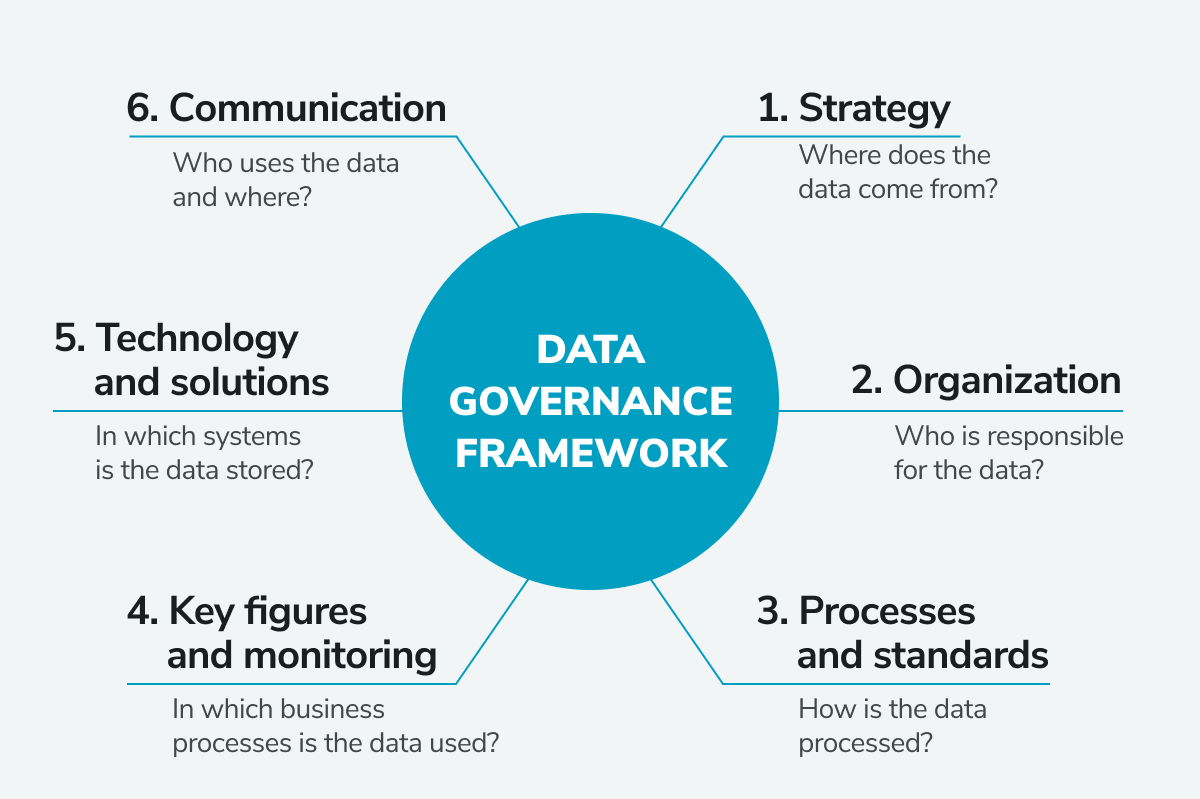 A data governance framework is essential for securing data
A data governance framework is essential for securing data
A data governance policy can be simple like protecting customer data by requiring employees to install VPNs on their laptops before using public Wi-Fi.
Or it could be a revised procedure that takes years to perfect as technology improves.
Many big companies use customer data for different reasons: product development, AI training, or insights on how to improve their service. But sensitive customer data can be challenging to obtain due to privacy laws.
In the past, legacy anonymization techniques were one alternative to accessing customer databases. However, companies are now moving away from these techniques and leaning more towards solutions like high-quality synthetic data generation, which can’t be re-identified and keeps customers’ privacy securely protected.
Regardless of the exact procedures you choose for your data governance framework, the key takeaway is that a robust data governance framework is essential to protect your brand from lawsuits, avoid losing customers over privacy issues or data breaches, and make sure that all employees are aware of their responsibilities regarding customers.
Practice data minimization
Data minimization is a practice that guarantees you’re only collecting the data you need to fulfill your business needs.
It’s essential for a few reasons:
- it protects your company from fines and regulations, like GDPR, by ensuring you’re not collecting more data than is necessary;
- it helps you track what kind of data you have and where it’s stored;
- it keeps a smaller amount of data stored on your servers if a breach does occur.
As the saying goes, less is more.
Focus on centralizing your data
You might have heard of data centralization, but what does it mean? Data centralization is when you move your data from multiple locations to a single source to minimize downtime, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
You can centralize your data using a data center infrastructure or a cloud solution.
Since you are storing your data in one central location, it’s crucial to back up regularly so that if something happens to one of your storage devices, you won’t lose any valuable information.
Also, it’s wise to consider granting particular entitlements so only authorized users can access specific files or documents. That way, if someone else gets their hands on one of your devices, they won’t be able to access all of your sensitive information without proper credentials.
Use data encryption where possible
Data encryption is a tool that can help you secure your sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII).
There are two main types of data encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt the data, while asymmetric encryption uses two keys — one to encrypt and one to decrypt.
Use an encrypted vault when storing sensitive information, such as PII or passwords. Encrypting this information with symmetric or asymmetric encryption will protect it from malicious actors if it’s stolen or compromised by hackers.
Make sure your passwords are strong. Weak passwords are easy for hackers to crack, which means they could gain access to your accounts, including those containing sensitive information like your PII.
By encrypting your data, you can get better security against hackers, Increased compliance with industry regulations, reduced liability for sensitive information exposed by accident or theft, and faster access to protected data.
Wrapping up
Customer data management is an evolving discipline. As the world becomes more digitized and new technologies emerge, it becomes increasingly important to know how to secure customer data. We hope this article has provided you with some insights into how to do that effectively to reduce the ever-looming stress of cybersecurity threats off your shoulders.
With a good customer data management strategy, you can improve efficiency, prevent data breaches, and set your business up for long-term success.